In the ever-evolving world of personal care, achieving the perfect balance of foam in rinse-off formulation is crucial for delivering superior performance in products.
We are excited to introduce our latest insights on how Alkyl Polyglucosides (APGs) can synergize with other surfactants to create exceptional foam properties. Let’s delve into the science behind foam fusion and how APGs can elevate your formulations to new heights.
The Science of Foam Fusion
Foam is more than just bubbles; it's a complex structure that plays a vital role in the sensory experience and efficacy of personal care products. The right foam can enhance the cleansing process, improve spreadability, and provide a luxurious feel. However, achieving the ideal foam requires a deep understanding of surfactant interactions.
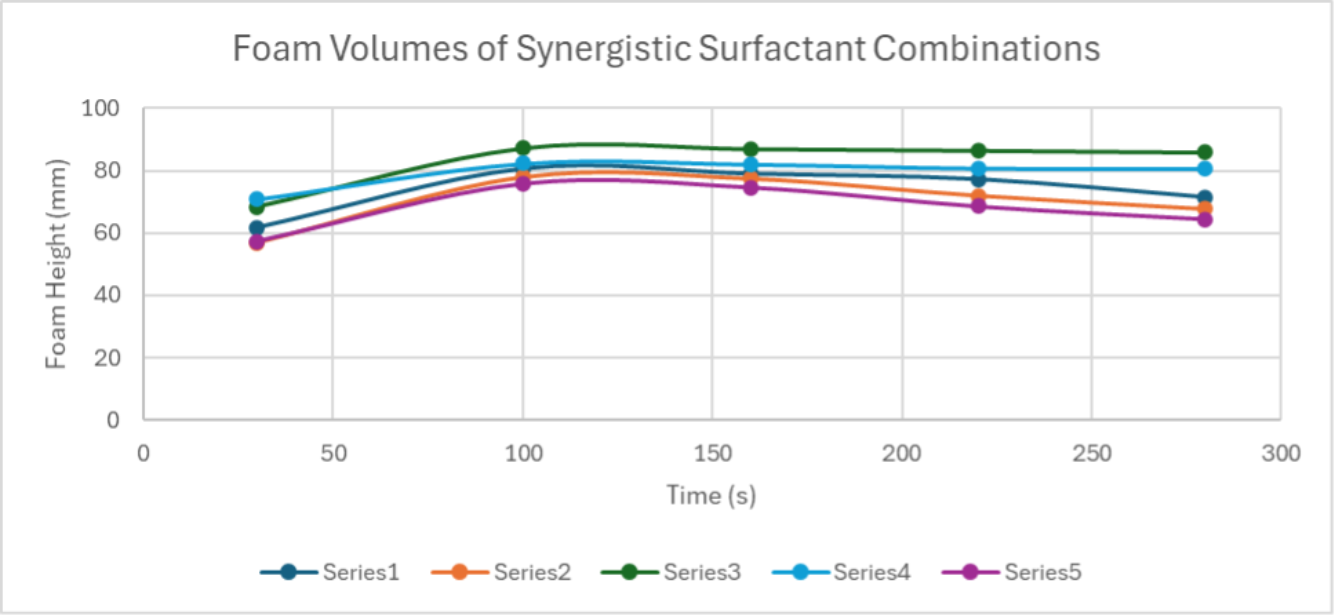
At BASF, we have explored the synergies between APGs and various cosurfactants, including Taurate, Isethionate, Glutamate, Glycinate, and Betaine. These combinations were carefully crafted by leveraging BASF’s digital tool, The Surfactant Navigator, which was an integral part in this project’s development. The physico-chemical measurements generated in Surfactant Navigator on the synergistic surfactant combinations include: foam volume, rate of foaming, foam decay, bubble size, and more, which link to great potential in optimizing foam and sensory characteristics for all rinse-off formulations. The graph below shows examples of the foam height (measured in volume) of APG synergistic combinations at various time points, compared to a traditional SLES/CAPB (Texapon N70/ Dehyton PK 45) combination.